Herpes: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment, and Prevention
Herpes is a viral infection affecting millions of people around the world. What exactly is herpes, its causes, symptoms and how can one treat it? Let’s find it out in this blog.
What is Herpes?
Herpes is a sexually transmitted viral infection caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV). There are two main types of this virus: HSV-1 and HSV-2. Both types cause infections in many areas of your body, but they are most commonly seen in the mouth and genital areas.
- HSV-1 is known to be responsible for causing oral herpes, which is seen as cold sores or fever blisters around your lips or inside your mouth.
- HSV-2 is mainly linked to genital herpes, which causes sores in the genital and anal areas.
However, both types of herpes can have effects on either area. For example, HSV-1 can cause genital herpes if it’s passed during oral sex, and HSV-2 can cause oral herpes in rare cases.
How Is Herpes Transmitted- Causes
Herpes is very contagious. It can spread even if the person is not showing any visible symptoms. That’s why it can be hard to tell when you might get exposed to the virus. Here are the main ways herpes can be transmitted:
-
- Direct skin-to-skin contact: with someone who has an active cold sore can actually transmit the infection to you- even if there is no sex.
- When You Share personal items: Items like towels, or drinking that have come in contact with the virus can also spread it.
- Asymptomatic shedding: This is when the virus is active and contagious, but the person doesn’t have any visible symptoms (like sores).
- Sex: All forms of sex can also lead to transmission
- Kissing: Can lead to oral herpes if one partner is infected.
- Childbirth: A mother with genital herpes can pass the virus to her baby during delivery and it can be dangerous for the newborn.
Signs and Symptoms of Herpes
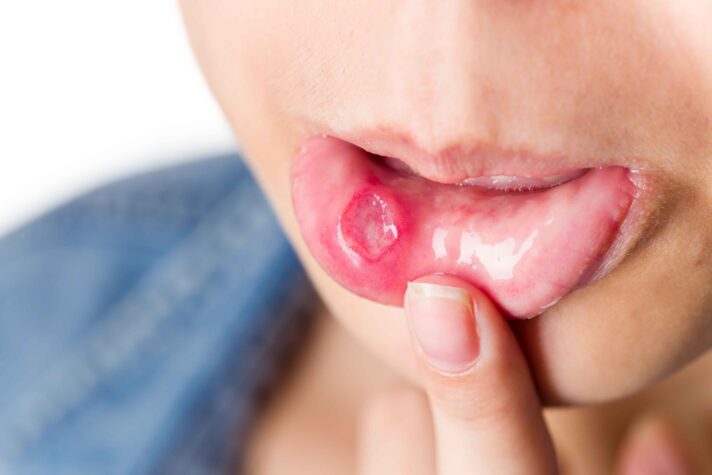
So how can you tell if you have herpes? Well, not everyone can see their symptoms, and when they do appear, it can range from mild to severe. The symptoms of herpes show up about 2 to 12 days after exposure. Here are some common symptoms:
- Cold sores or blisters (on the lips, mouth, or genital area)
- Pain or itching around the affected area before blisters appear
- Painful urination (in the case of genital herpes)
- Flu-like symptoms like fever, body aches or swollen lymph nodes, mainly during the first outbreak
- Genital or anal sores that come as small, fluid-filled blisters
The first outbreak is the most severe stage. After the first outbreak, the virus can lie dormant in the body and reactivate later, triggered by stress, other illnesses, or other factors in incidences commonly referred to as “Flare-Ups”
How is Herpes Diagnosed?
If you think you have herpes or have had contact with someone who has it, the first thing you should do is see a sexual health expert. Herpes is diagnosed by:
- Physical examination: A doctor will look at your sores or blisters and ask you about your symptoms.
- Swab test: If there’s a recent outbreak, your doctor might take a swab from the sore and send it to a lab to confirm the herpes virus infection.
- Blood test: If you don’t have any visible sores, a blood test can detect antibodies to the herpes virus, which confirms past infection.
Working with a doctor is the best way to get a confirmed diagnosis whether you have symptoms or not.
Allo Health has helped more than 75,000 patients with sexual health concerns including Herpes testing and treatment.
Treatment and Solutions for Herpes
Herpes currently has no cure. If infected you may face symptoms and flare ups from time to time. But there are many ways to manage the symptoms and reduce the severity and frequency of outbreaks. Here are some treatment options:
-
- Antiviral medication: keep a check on the severity of outbreaks, speed up healing, and lower the risk of transmitting the virus to others.
- Topical creams: Using over-the-counter creams or prescription medications for your cold sores to reduce pain.
- Pain relief: Over-the-counter pain relievers might help you with the pain, and ice packs can soothe the affected area.
- Therapy: Dealing with herpes outbreaks can be anxiety inducing and stressful and may affect your overall perception of sexuality- working with an informed sexual health therapist can help you cope with these feelings and navigate a healthy sex life.
Researchers are also developing mRNA vaccines to target herpes simplex virus, similar as COVID-19 vaccines. These vaccines trigger an immune response against the virus and prevent outbreaks. One study from 2023 talked about the potential of mRNA-based vaccines for both genital herpes and oral herpes.
Work under close guidance of your healthcare provider to understand what medication can help you relieve pain and discomfort. Allo Health doctors & therapists are amongst the leading providers for sexual health & STI care in India.
How to Prevent Herpes

Here are some tips to reduce the risk of getting herpes or spreading it:
- Use protection: Use condoms or dental dams to keep check on the transmission during sexual activity.
- Don’t have any sexual contact during outbreaks: If you or your partner has some visible sores or symptoms, give a break to sexual contact until the outbreak has passed.
- Talk with your partner: Talk it out with your partner about herpes and safe sex practices. It will keep you informed and protect both of you.
- Try to take antiviral medication: If you have frequent outbreaks, your doctor may recommend taking antiviral medication daily to reduce any risk of spreading the virus.
How Herpes Affects Intimate Relationships
When you get herpes, it doesn’t mean you can’t have any more intimate relationships. It may come with some challenges. about herpes with their partner. The stigma around herpes gives anxiety or stress, which can affect the relationship.
But here’s the thing: herpes can happen to anyone, and many people have it without even knowing. If you have herpes, talk with your partner. You can still have a fulfilling intimate relationship by trying to prevent spreading the virus- avoid sexual activity during an outbreak, always use protection (condoms), and start taking antiviral medication (only on doctor’s recommendation) to reduce the risk of transmission.
Many couples find that with trust, understanding, and safe sexual practices, herpes doesn’t quite interfere with their relationship.
Note: If your Herpes continues and keeps affecting your quality of life or relationships, it’s important to consult a sexual health professional. You can now consult a sexual health doctor at any one of 20 Allo Sexual Health Clinics for a full diagnosis at just Rs. 499 or through an online consultation at just Rs. 199.
Key Takeaway
- Herpes is a viral infection caused by two types of herpes simplex viruses (HSV): HSV-1 and HSV-2. HSV-1 typically causes oral herpes (cold sores), while HSV-2 is more commonly associated with genital herpes. However, both types can affect either area through direct contact.
- It’s estimated that around 67% of the global population under 50 has HSV-1, and about 11% of people worldwide have HSV-2. Despite its high prevalence, many people with herpes don’t show symptoms or are unaware they are infected.
- You can get herpes even when there are no obvious sores or symptoms, which is why it’s so easily transmitted.
- While there’s no cure for herpes, antiviral medications can help manage the symptoms and reduce the frequency of outbreaks. Medications like acyclovir, valacyclovir, and famciclovir can also lower the risk of spreading the virus to others.
"The following blog article provides general information and insights on various topics. However, it is important to note that the information presented is not intended as professional advice in any specific field or area. The content of this blog is for general educational and informational purposes only.
Book consultation
The content should not be interpreted as endorsement, recommendation, or guarantee of any product, service, or information mentioned. Readers are solely responsible for the decisions and actions they take based on the information provided in this blog. It is essential to exercise individual judgment, critical thinking, and personal responsibility when applying or implementing any information or suggestions discussed in the blog."