How Is Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID) Diagnosed?

Allo Health is dedicated to personalized well-being, offering support and trusted information tailored to individual health goals. The platform emphasizes human-generated content, led by a distinguished medical team of experts, including physicians and sexual health specialists. Their commitment to credibility involves rigorous fact-checking, authoritative research, and continuous updates to ensure accurate, up-to-date information. Allo Health's unique approach goes beyond conventional platforms, providing expert-led insights and a continuous commitment to excellence, with user feedback playing a crucial role in shaping the platform's authoritative voice.

Dr Sanina Mansoor holds MBBS degree from Yenepoya university,Mangalore.She has 8 years of experience working as a medical officer at various health centres and medical colleges.
Why This Was Upated?
Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information became available.
Updated on 20 June, 2025
- Article was updated as part of our commitment to diversity, equity, and inclusion.

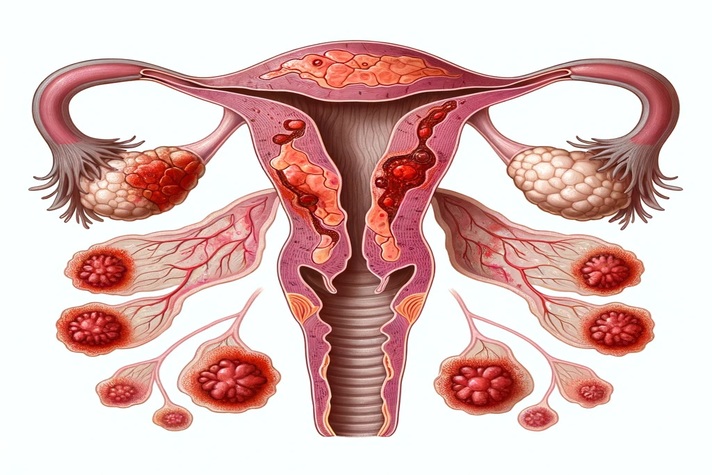
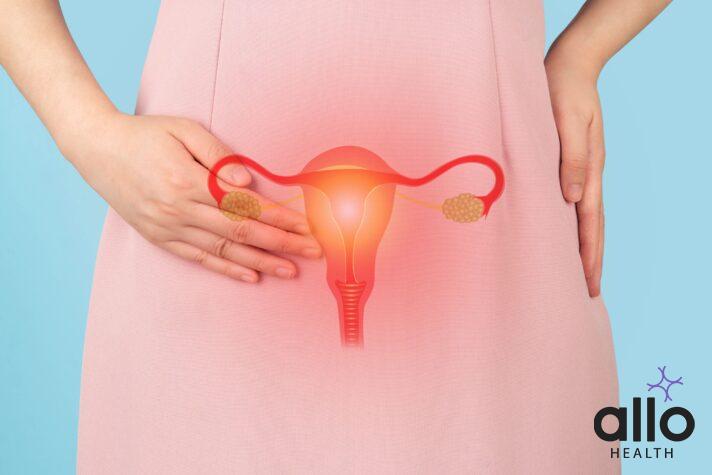
Diagnosing Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID) involves a comprehensive approach that combines medical history assessment, physical examination, laboratory tests, and sometimes imaging studies. PID is a serious infection of the female reproductive organs, primarily caused by bacteria that enter the reproductive tract. Prompt and accurate diagnosis of PID is crucial for effective treatment and prevention of complications. Here, we will explore the various methods and procedures used in the diagnosis of PID.
Medical History Assessment
- Symptoms Inquiry: Healthcare providers start by gathering information about the patient’s symptoms, including lower abdominal or pelvic pain, abnormal vaginal discharge, painful urination, painful intercourse, irregular menstrual bleeding, fever, and fatigue. The patient’s sexual history, contraceptive methods, and recent infections or procedures are also assessed.
- Risk Factors Evaluation: Assessment of risk factors such as multiple sexual partners, history of sexually transmitted infections (STIs), recent insertion of intrauterine devices (IUDs), and previous episodes of PID help in determining the likelihood of PID.
Physical Examination
- Pelvic Examination: A pelvic examination is a crucial part of PID diagnosis. During the exam, the healthcare provider inspects the external genitalia, vagina, cervix, uterus, and ovaries for signs of infection or inflammation.
They may note tenderness, swelling, abnormal discharge, or cervical motion tenderness (pain with movement of the cervix). - Speculum Examination: A speculum is inserted into the vagina to visualize the cervix and collect samples for laboratory testing. The appearance of the cervix, discharge, and presence of lesions or abnormalities are assessed.
Laboratory Tests
- Vaginal Swabs: Samples of vaginal discharge or cervical secretions are collected using swabs for laboratory analysis. These samples are examined for the presence of infectious organisms, particularly bacteria commonly associated with PID, such as Chlamydia trachomatis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae.
- Cervical Cultures: Cultures may be performed to identify specific bacterial pathogens causing PID. The samples obtained from the cervix are cultured in a laboratory to isolate and identify bacteria, providing information on antibiotic susceptibility for targeted treatment.
- Urine Tests: Urine samples may be tested for signs of infection, including white blood cells (indicative of inflammation) and bacteria. Urine tests can help rule out urinary tract infections (UTIs) and assess the extent of systemic involvement in PID cases.
- Blood Tests: Blood tests may be ordered to evaluate inflammatory markers such as C-reactive protein (CRP) and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR). Elevated levels of these markers indicate an inflammatory response, supporting the diagnosis of PID.
Imaging Studies

- Pelvic Ultrasound: In some cases, pelvic ultrasound imaging may be performed to visualize the reproductive organs and assess for abnormalities such as fluid collections (abscesses), thickened fallopian tubes, or other structural changes suggestive of PID complications. Trans-vaginal ultrasound provides detailed images of the pelvic organs.
Diagnostic Criteria
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) have established clinical criteria for diagnosing PID, known as the “CDC criteria.” These criteria include the presence of lower abdominal or pelvic pain, cervical motion tenderness on pelvic examination, uterine or adnexal tenderness on pelvic examination, and additional findings such as abnormal cervical or vaginal discharge, fever, elevated inflammatory markers, or positive laboratory tests for STIs.
Differential Diagnosis
PID shares symptoms with other gynaecological and pelvic conditions, making differential diagnosis essential. Conditions that may mimic PID include urinary tract infections (UTIs), ovarian cysts, ectopic pregnancy, endometriosis, appendicitis, and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Healthcare providers use a combination of history, physical examination findings, laboratory tests, and imaging studies to differentiate PID from other conditions accurately.
Diagnosing Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID) requires a comprehensive approach that integrates medical history assessment, physical examination, laboratory tests (vaginal swabs, cervical cultures, urine tests, blood tests), and sometimes imaging studies (pelvic ultrasound). The CDC criteria for PID diagnosis provide a standardized framework based on clinical findings and laboratory results. Prompt diagnosis and initiation of appropriate antibiotic treatment are essential to reduce the risk of complications and preserve reproductive health. If you suspect you may have PID or have concerns about your reproductive health, seek medical evaluation from a healthcare provider for accurate diagnosis and personalised management.
"The following blog article provides general information and insights on various topics. However, it is important to note that the information presented is not intended as professional advice in any specific field or area. The content of this blog is for general educational and informational purposes only.
Book consultation
The content should not be interpreted as endorsement, recommendation, or guarantee of any product, service, or information mentioned. Readers are solely responsible for the decisions and actions they take based on the information provided in this blog. It is essential to exercise individual judgment, critical thinking, and personal responsibility when applying or implementing any information or suggestions discussed in the blog."