Fluoxetine (Prozac) and Erectile Dysfunction: Uses, Dosage, and Sexual Side Effects
Written by Dr. Pranitha Bangera

Dr. Pranitha Bangera is a gold-medalist healthcare professional with an elite foundation in clinical training and patient care. A researcher at heart, she specializes in creating high-impact, research-driven medical content that empowers readers through accessible patient education. Dr. Bangera focuses on the intersection of digital health and clinical communication, specifically within the fields of sexual health and mental well-being. Her work is dedicated to making complex medical innovations understandable and trustworthy for a global audience.
•
December 9, 2025
Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information becomes available.
Quick Read
Fluoxetine (Prozac) is an effective SSRI used to treat depression, anxiety, OCD, and other mental health conditions, but it can also cause sexual dysfunction, including erectile dysfunction. This happens because the medication increases serotonin, which can lower dopamine, reduce blood flow, and affect penile tissue relaxation, all important for a healthy sexual response. The underlying conditions fluoxetine treats can also contribute to ED, making it a combined effect for many men. The good news is that fluoxetine-related ED is usually reversible. Recovery depends on dose, duration, and individual sensitivity, and most people improve after adjusting medication or adding targeted treatments. With the right support from a doctor or sexual-health specialist, most men can continue benefiting from fluoxetine while regaining healthy sexual function and confidence.
Fluoxetine, commonly known by the brand name Prozac, is one of the most widely prescribed medications (selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors) for conditions like depression and social anxiety disorder. However, like most antidepressant drugs, fluoxetine can also cause erectile dysfunction (ED). Fluoxetine can affect sexual function by increasing serotonin levels, which may slow down the sexual response and reduce arousal. It can also indirectly lower dopamine, a key chemical involved in desire and erection maintenance. In some men, it may interfere with nitric oxide, the chemical responsible for penile blood flow, and make it harder for the erectile tissue to relax fully. Together, these effects can lead to changes in libido, performance, and erection quality. In this article, we’ll break down the evidence, the mechanisms, how long these effects last, and what can be done to improve erectile function while continuing necessary treatment.
Allo asks
If you experienced ED on fluoxetine, what would you consider first?
Does Fluoxetine Cause Erectile Dysfunction?
Research shows clearly that fluoxetine can cause erection problems in a significant percentage of users. Early clinical trials reported very low rates (around 1–2%), but these weren't accurate as people were rarely asked about sexual side effects. [1] When modern studies used structured questionnaires, a very different picture emerged:
- 46–58% of fluoxetine users reported some form of sexual dysfunction[2]
- 10–34% of men reported erectile dysfunction specifically[2]
- Another study found 66.7% of men experienced sexual dysfunction while taking fluoxetine[3]
Compared to other drugs, fluoxetine sits in the middle range. Paroxetine is known for the highest sexual side effects, while medications like escitalopram and sertraline show similar rates to fluoxetine.
How Does Fluoxetine Cause Erectile Dysfunction?
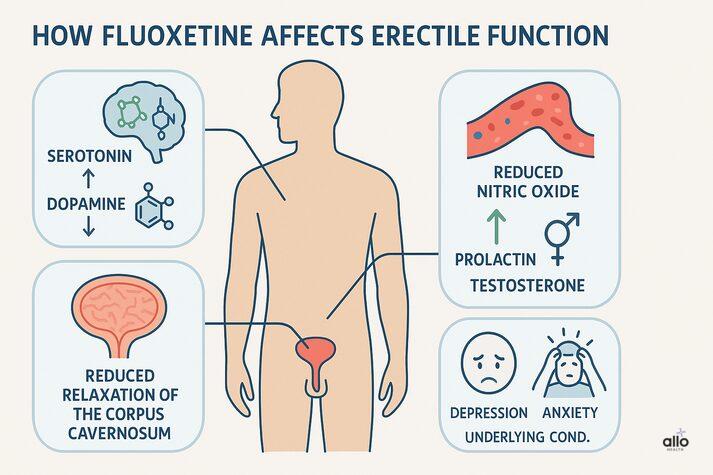
Erectile function depends on a balanced interaction between hormones, brain chemicals, blood vessels, and sexual arousal. Fluoxetine can influence several parts of this system:
1. Effects on Penile Tissue
Studies suggest fluoxetine can make it harder for the spongy tissue in the penis to relax, which is an important step needed for a firm erection, thus affecting the mechanics of erection itself. [4]
2. Reduced Blood Flow to the Penis
Erections depend heavily on nitric oxide, a chemical that helps blood to flow into the penis. Some SSRIs interfere with the production of nitric oxide, thus decreasing how much of it is available in the body to help with erections.[5]
3. Brain Chemical Imbalance
Fluoxetine increases serotonin, a key chemical that supports good mood, by blocking its “reuptake.” Reuptake is the brain’s natural cleanup process, where nerve cells absorb serotonin back after it’s released. When fluoxetine stops this absorption, more serotonin stays active for longer. This helps improve mental health, but higher serotonin levels can also slow down the sexual response and make erections harder to achieve. This is true for all drugs that fall under the category of serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), not just fluoxetine. [6] High serotonin can indirectly lower dopamine, the brain chemical responsible for sexual desire, sexual motivation, and erection maintenance. Low dopamine can make it harder to initiate sexual behavior or maintain an erection. [6]
4. Hormonal Imbalance
Prolactin is a hormone made by the pituitary gland that, when elevated, can lower dopamine levels and disrupt sexual desire and erection quality. It can also interfere with testosterone, the male hormone responsible for sex drive.[7]
5. Underlying Conditions
The conditions fluoxetine treats, such as depression, anxiety, OCD, social anxiety disorder, and PTSD, can themselves contribute to erectile dysfunction. Low mood and reduced dopamine in depression can weaken sexual desire, while anxiety and panic increase stress hormones that tighten blood vessels and make erections harder to achieve. Intrusive thoughts, fear of intimacy, and emotional tension can also interfere with arousal and the ability to stay present during sexual activity. This means ED can come from the underlying condition, the medication, or a mix of both, which is why understanding how fluoxetine affects sexual function becomes especially important.
Is Erectile Dysfunction Caused by Fluoxetine Permanent?
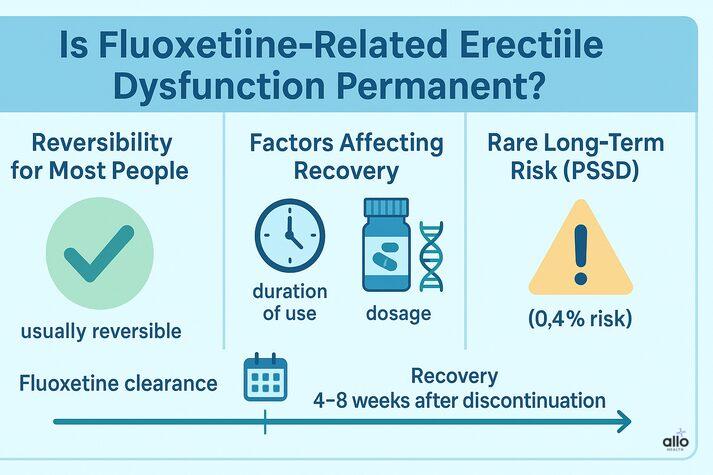
Fortunately, fluoxetine-related erectile dysfunction is usually reversible.
What determines recovery?
- Duration of use: Short-term users often recover faster
- Dosage: Higher doses carry a higher risk
- Individual sensitivity: Genetics and hormone levels can influence effects [6]
In one study:
- Only 5.8% of patients saw spontaneous recovery without medication changes
- Most experienced no improvement until treatment was adjusted [6]
This means the ED associated with antidepressant use of fluoxetine often does not resolve on its own.
Is there a risk of long-term effects?
A small percentage of patients may develop post-SSRI sexual dysfunction (PSSD), where they experience persistent symptoms even after stopping the medication. This is rare (estimated at around 0.4%), but worth mentioning during treatment discussions. [6]
When does ED improve after stopping fluoxetine?
Fluoxetine has a long half-life, so full clearance can take several weeks. Animal studies show reproductive recovery within 4–8 weeks after discontinuation. [6]
Sexual Side Effects of Fluoxetine in Men
While erectile dysfunction gets the most attention, fluoxetine may also cause:
- Decreased libido or reduced sexual desire
- Delayed ejaculation
- Difficulty achieving orgasm (anorgasmia)
- Genital anesthesia (reduced sensitivity)
- Decreased morning erections
- Lower overall sexual satisfaction [6]
These effects relate to altered serotonin-dopamine balance and slowed sexual response.
When to See a Doctor
It’s important to consult a clinician if you experience:
- New or worsening sexual dysfunction
- Erectile failure lasting more than 4–6 weeks
- Suddenly, severe sexual side effects after dose changes
- Reduced quality of life or distress about sexual performance
A doctor can help confirm whether symptoms are caused by:
- The medication
- The underlying depression
- Stress
- Relationship issues
- Physical health conditions like high blood pressure, diabetes, or heart disease
Sexual side effects are one of the top reasons people stop antidepressant treatment. This is where a conversation with a general practitioner or mental health specialist becomes essential, because untreated depression itself is linked to ED and changes in sexual behavior. Note: Never stop antidepressants abruptly; drug cessation without supervision can worsen mental health.
How to Manage Erectile Dysfunction Caused By Prozac
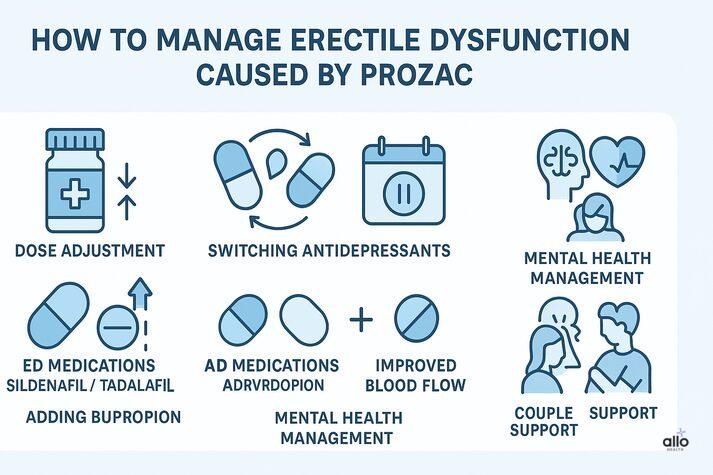
1. Dose Adjustment
Sexual side effects are often dose-dependent. Your doctor may:
- Reduce the daily dose
- Adjust the timing of the dose
- Switch from daily to alternate-day dosing
2. Switching Antidepressants
If ED is persistent, switching to an antidepressant with fewer sexual side effects may help. Options include:
- Bupropion (strongest evidence for improving sexual function)
- Mirtazapine
- Agomelatine
- Moclobemide
- Vortioxetine (lower risk compared to SSRIs)
Switching between SSRIs rarely solves ED because the mechanisms are similar.
3. “Drug Holiday” for Fluoxetine
Some doctors may recommend pausing the drug briefly before expected sexual activity. This must be done under medical guidance and is not recommended for all antidepressants.
4. ED Medications
Medications like sildenafil citrate (Viagra), tadalafil, and vardenafil are commonly used to treat SSRI-induced erectile dysfunction. They work by enhancing nitric oxide and improving blood flow to the penis. A clinician will check for:
- Heart disease
- High blood pressure
- Interactions with other medications, such as nitrates or beta blockers
5. Adding Bupropion
Some mental health specialists add bupropion alongside fluoxetine to counter sexual side effects.
6. Managing Mental Health
- Address anxiety around sexual performance
- Improve sleep, stress management, and physical activity
- Strengthen emotional intimacy with a partner
- Address depression symptoms, which also contribute to ED
People often find it reassuring to talk to a sexual-health trained clinician who understands the overlap between mental health and erectile dysfunction. Integrating support for both can lead to better outcomes.
Fludac 20 for Erectile Dysfunction
Fludac 20 is an Indian brand of fluoxetine 20 mg. Because it contains the same active ingredient as Prozac, it carries the same risk of sexual side effects, including erectile dysfunction, decreased libido, and delayed ejaculation. If someone experiences ED on Fludac 20:
- The management strategies are identical
- Dose adjustments or switching antidepressants may help
- ED medications may improve erectile function
The key steps remain open communication with a clinician and careful adjustment of treatment.
How to Prevent Erectile Dysfunction From Prozac
1. Start with the lowest effective dose
This reduces the chances of early-onset sexual side effects.
2. Monitor sexual function early
Tracking changes helps your general practitioner adjust treatment before symptoms worsen.
3. Lifestyle Changes
Regular exercise and a balanced diet supporting vascular health can improve erectile function.
4. Address stress and relationship factors
A healthy emotional connection enhances sexual desire and responsiveness. Psychotherapy for ED combined with CBT for underlying issues can help improve overall sexual and mental health.
Think of fluoxetine as helping one system while temporarily slowing down another. Our goal is to find the dose or treatment plan where your mood improves without affecting your sexual health.
Conclusion
Fluoxetine is a valuable antidepressant that helps millions of people manage depression, anxiety, and other mental health conditions. But like many SSRIs, it can cause sexual side effects, including erectile dysfunction, changes in libido, and delayed ejaculation. These effects can feel frustrating, but they are common, well-understood, and often reversible. With thoughtful medical guidance, evidence-based management strategies, and attention to both mental and sexual well-being, most people can continue benefiting from fluoxetine while restoring healthy sexual function. If symptoms persist, speaking to a clinician is the best first step.
Disclaimer
The following blog article provides general information and insights on various topics. However, it is important to note that the information presented is not intended as professional advice in any specific field or area. The content of this blog is for general educational and informational purposes only. The content should not be interpreted as endorsement, recommendation, or guarantee of any product, service, or information mentioned. Readers are solely responsible for the decisions and actions they take based on the information provided in this blog. It is essential to exercise individual judgment, critical thinking, and personal responsibility when applying or implementing any information or suggestions discussed in the blog.
Most Asked Questions
How common is ED with fluoxetine?
Studies show that sexual side effects happen in 30–50% of people taking SSRIs, including fluoxetine. Not everyone experiences ED, but it is a well-recognised and documented side effect.
Is ED from fluoxetine permanent?
In most cases, no. ED caused by fluoxetine is usually temporary and improves with dose adjustments, switching medications, or using ED treatments. Only a very small percentage may experience persistent symptoms.
Will ED go away if I stop taking fluoxetine?
For many men, sexual function improves within a few weeks after the medication is stopped. However, you should never stop an antidepressant suddenly. Always talk to your doctor before making changes to your dose.
Can I take Viagra with fluoxetine?
Yes, doctors often prescribe sildenafil (Viagra) or other PDE5 inhibitors to treat SSRI-related ED. These medications are generally safe when used correctly, but a doctor should check for heart conditions or medication interactions first.
What if my ED is from depression, not Prozac?
Both depression and fluoxetine can affect sexual function. Depression can lower libido, increase anxiety, and disrupt arousal. A doctor can help determine the main cause and adjust treatment accordingly.
Sources
- 1.
Resolution of Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitor–Associated Sexual Dysfunction After Switching From Fluvoxamine to Fluoxetine
- 2.
Fluoxetine-induced sexual dysfunction and an open trial of yohimbine
- 3.
Antidepressant-Induced Sexual Dysfunction among Newer Antidepressants in a Naturalistic Setting
- 4.
Pulmonary, Gastrointestinal and Urogenital Pharmacology Chronic administration of fluoxetine impairs neurogenic and endothelium-dependent relaxation of the rabbit corpus cavernosum smooth muscle
- 5.
Differential effects of serotonin reuptake inhibitors on erectile responses, NO-production, and neuronal NO synthase expression in rat corpus cavernosum tissue
- 6.
Mechanisms and treatments of SSRI-induced sexual dysfunction
- 7.
HYPERPROLACTINEMIA AND MALE SEXUAL FUNCTION: FOCUS ON ERECTILE DYSFUNCTION AND SEXUAL DESIRE


