Antihistamines and Erectile Dysfunction: Do Allergy Meds Affect Sex?
Written by Dr. Pranitha Bangera

Dr. Pranitha Bangera is a gold-medalist healthcare professional with an elite foundation in clinical training and patient care. A researcher at heart, she specializes in creating high-impact, research-driven medical content that empowers readers through accessible patient education. Dr. Bangera focuses on the intersection of digital health and clinical communication, specifically within the fields of sexual health and mental well-being. Her work is dedicated to making complex medical innovations understandable and trustworthy for a global audience.
•
October 24, 2025
Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information becomes available.

Quick Read
Yes, certain antihistamines can cause erectile dysfunction (ED) by blocking histamine — a chemical that supports sexual arousal and blood flow — and by affecting hormones like testosterone and prolactin. Older, sedating allergy medicines are more likely to cause these side effects, while newer ones are generally safer. The good news: in most cases, antihistamine-related ED is temporary and reversible once medication is adjusted or stopped. Always consult your doctor before changing any prescription, and maintain healthy habits to support both allergy control and sexual wellness.
Allergies can be frustrating enough on their own, with constant sneezing, itchy eyes, and congestion, which can be exhausting. But for some men, there’s an unexpected side effect that’s even more concerning: erectile dysfunction. Research suggests that certain antihistamines, the medications used to control allergy symptoms, may cause ED. This happens because they block histamine, a chemical that helps with sexual arousal and blood flow to the penis. They also cause drowsiness, making it harder to stay physically and mentally engaged during sex. In this article, we’ll explore how antihistamines work, why they might affect erections, which types are more likely to cause problems, and what you can do to prevent or manage these effects.
Allo asks
Have you noticed changes in your sexual performance after taking allergy medication?
Do Antihistamines Cause Erectile Dysfunction?
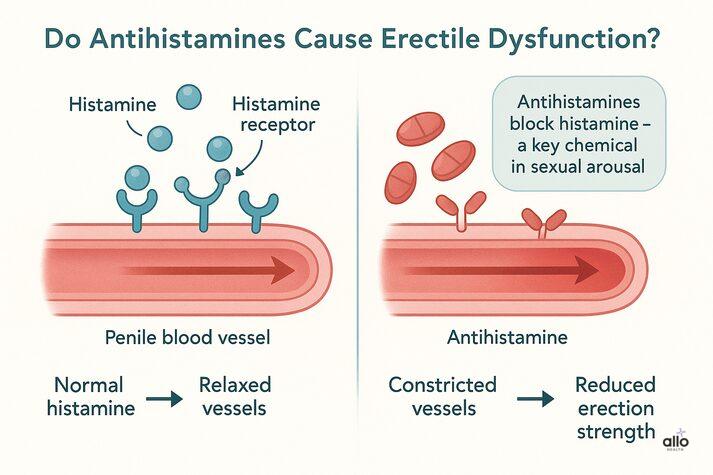
Yes, some antihistamines can cause erectile dysfunction. These medicines block histamine, a natural chemical that not only triggers allergic reactions but also plays a role in sexual arousal. When this hormone is blocked, it can lead to weaker or less consistent erections. Some studies suggest that long-term or high-dose use of these drugs can affect testosterone production, which is the key male hormone responsible for sex drive. [1] Research also shows that it can reduce blood flow to the penis, making it harder to achieve an erection. [2] Let's look at how this happens in detail.
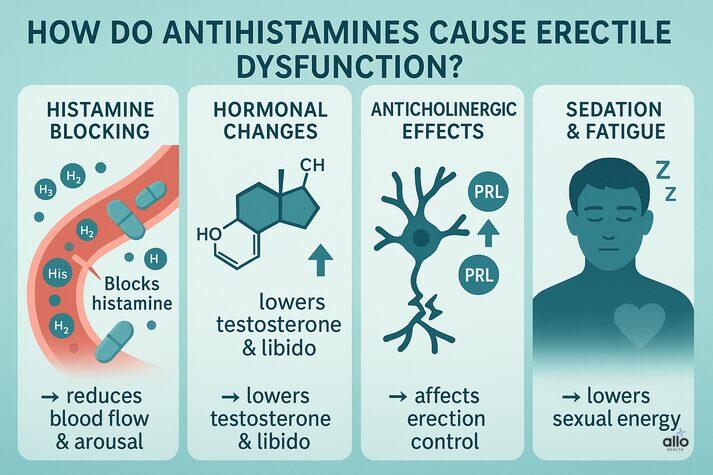
How Do Antihistamines Cause Erectile Dysfunction?
Antihistamines can interfere with normal sexual function in the following ways:
1. Histamine Blocking:
Histamine is involved in the process of sexual arousal and blood vessel relaxation. [3] These drugs block histamine receptors, which are like tiny “switches” in your body that respond to histamine. [4] Due to this, it may indirectly restrict blood flow to the penis and affect sexual arousal.
2. Hormonal Changes:
Certain antihistamines, like cimetidine (Tagamet), can interfere with testosterone production [5]. They can also increase prolactin levels. [6] When prolactin levels get too high in men, it can lower testosterone. [7] These hormonal changes may reduce libido and contribute to sexual dysfunction.
3. Anticholinergic Effects:
Many antihistamines block acetylcholine, a brain chemical that is essential for nerve communication and muscle function.[8]. This can lead to poor nerve signaling and limited blood circulation in the penile area, worsening antihistamine erectile dysfunction.
4. Sedation and Fatigue:
Drowsiness and mental sluggishness caused by these medications can reduce sexual arousal and performance. [4]
Do All Antihistamines Cause Erectile Dysfunction?
No, not all antihistamines cause erectile dysfunction, but some are more likely to affect sexual health than others. Older drugs are more likely to interfere with hormones, blood flow, and nerve signaling linked to sexual arousal, while newer options are generally safer.
Type
Examples
Effect on Erectile Function
H₂ Receptor Antagonists
Cimetidine (Tagamet), Ranitidine (Zantac)
- Reduces testosterone production
- Increases prolactin levels
First-Generation Antihistamines
Diphenhydramine (Benadryl), Dimenhydrinate (Dramamine), Hydroxyzine (Vistaril), Promethazine (Phenergan)
- Strong anticholinergic effects
- Causes drowsiness
Second-Generation Antihistamines
Loratadine (Claritin), Cetirizine (Zyrtec), Fexofenadine (Allegra)
- Safer for long-term use
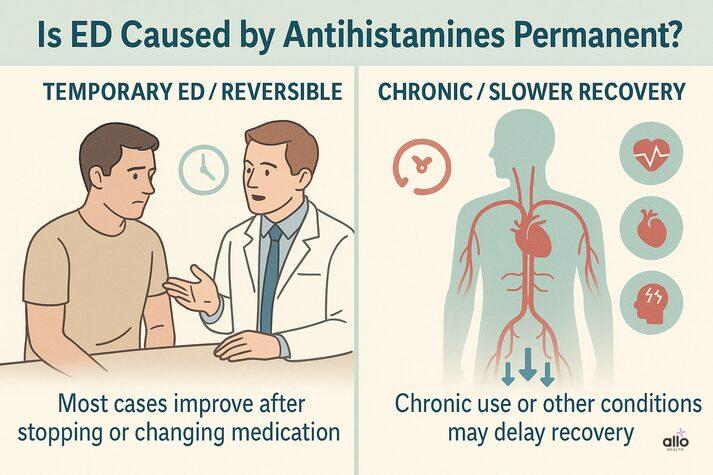
Is ED Caused by Antihistamines Permanent?
In most cases, antihistamine-induced erectile dysfunction is temporary and reversible. Once the medication is stopped or switched, sexual function often returns to normal. However, chronic use or high doses may take longer to resolve. [1] It’s also important to remember that other factors, like high blood pressure, cardiovascular disease, or psychological factors (such as stress and anxiety), can worsen the problem and slow recovery.
How to Prevent ED Caused By Antihistamines?
If you’re taking antihistamines and notice sexual side effects, here are steps to prevent them:
1. Consult Your Doctor:
Your doctor may adjust your dose or switch you to a different antihistamine with fewer side effects. For example, moving from diphenhydramine to fexofenadine may help.
2. Use Non-Drug Allergy Relief:
Try nasal saline sprays, air purifiers, hypoallergenic bedding, or allergy shots. These reduce reliance on daily medication.
3. Time Your Dose Wisely:
Taking short-acting antihistamines earlier in the day may help minimize interference with sexual activity at night.
4. Address Other Risk Factors:
Manage high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and heart disease, as these can all contribute to ED.
5. Adopt Healthy Habits:
Regular exercise, losing weight, a healthy diet, quitting smoking, and good sleep can naturally improve blood flow and support erectile function. Note: Always consult your doctor before stopping or switching any medication.

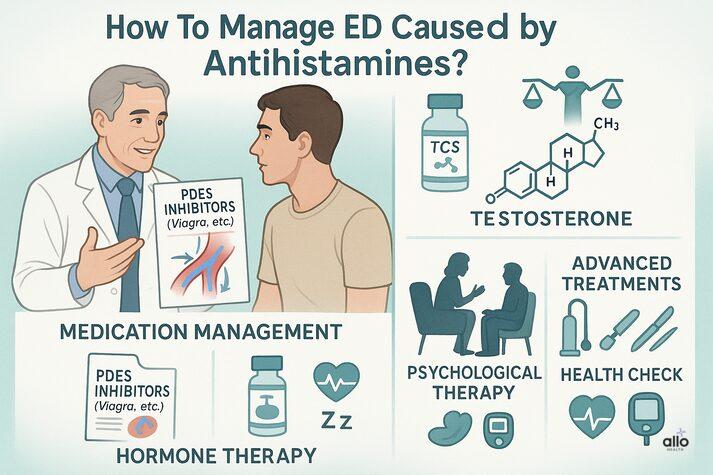
How To Manage ED Caused by Antihistamines?
If ED persists even after adjusting your antihistamine use, doctors may recommend:
- ED medications like PDE5 inhibitors (eg, Viagra ) to increase blood flow.
- Hormone therapy medications are used if testosterone deficiency is detected.
- Psychotherapy is used when psychological factors like anxiety or depression play a role.
- In advanced cases, options like a penis pump, penile implants, or surgery may help.
Your healthcare provider might also check for related heart conditions, metabolic syndrome, or sleep disorders, as these can overlap with antihistamine erectile dysfunction and make treatment less effective.
If you’re experiencing ED after taking allergy medication, don’t panic. There are safer, newer antihistamines you can use to manage allergies without compromising sexual health.
Conclusion
Antihistamines are effective for managing allergic diseases like allergic rhinitis, but they’re not entirely free from side effects. While most men won’t experience problems, some may notice symptoms of antihistamine erectile dysfunction, especially with older or higher-dose medications. The good news is that this side effect is often reversible and manageable with proper medical guidance. If you experience persistent sexual dysfunction, talk to your doctor. With the right adjustments and healthy lifestyle choices, most men can restore normal sexual performance while still keeping allergies under control.
Disclaimer
The following blog article provides general information and insights on various topics. However, it is important to note that the information presented is not intended as professional advice in any specific field or area. The content of this blog is for general educational and informational purposes only. The content should not be interpreted as endorsement, recommendation, or guarantee of any product, service, or information mentioned. Readers are solely responsible for the decisions and actions they take based on the information provided in this blog. It is essential to exercise individual judgment, critical thinking, and personal responsibility when applying or implementing any information or suggestions discussed in the blog.
Most Asked Questions
Can antihistamines cause erectile dysfunction?
Yes, some antihistamines can contribute to erectile dysfunction (ED). They work by blocking histamine, a chemical involved in both allergic reactions and sexual arousal. This can temporarily reduce blood flow and sensitivity needed for an erection.
Which antihistamines are most likely to cause ED?
Older, first-generation antihistamines like diphenhydramine (Benadryl), promethazine (Phenergan), and hydroxyzine (Vistaril) are more likely to cause ED. Newer, second-generation options such as fexofenadine (Allegra) or loratadine (Claritin) are generally safer.
How do antihistamines interfere with sexual function?
They can affect sexual function by blocking histamine receptors, reducing testosterone, and increasing prolactin levels, which may lower libido. Some also cause drowsiness and fatigue, making arousal more difficult.
Can I prevent ED while taking allergy medicine?
Yes. Take the lowest effective dose, avoid sedating antihistamines if possible, and discuss alternatives like fexofenadine with your doctor. Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and stress management also help maintain sexual health.
Should I stop taking my antihistamine if I notice ED?
Don’t stop on your own. Talk to your doctor first — they can adjust your dosage, suggest a different antihistamine, or explore other causes of ED such as stress, sleep loss, or heart health.
Sources
- 1.
Potential negative effects of anti-histamines on male reproductive function
- 2.
The role of histamine in human penile erection
- 3.
Characterization and function of histamine receptors in corpus cavernosum
- 4.
Pharmacology of Antihistamines
- 5.
Cimetidine Blocks Testosterone Synthesis
- 6.
CIMETIDINE, AN H2-ANTIHISTAMINE, STIMULATES PROLACTIN SECRETION IN MAN
- 7.
Hyperprolactinemia and Erectile Dysfunction
- 8.
Comparative anticholinergic activities of 10 histamine H1 receptor antagonists


